Modal
Also known as: Pop-up window
Modals focus the user’s attention exclusively on one task or piece of information via a window that sits on top of the page content. They require the user to take an action.
Examples
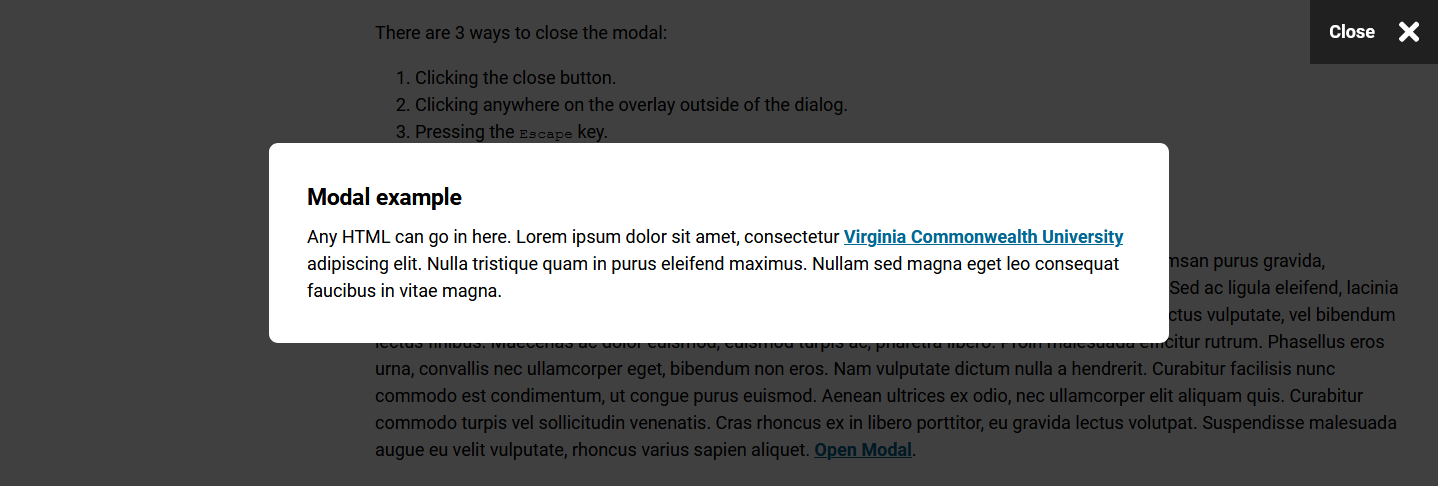
Example link
- Open the example modal.
When to use
Modals are ideal for:
- Revealing critical information: Show important details without navigating away from the current page.
- Maintaining context: Provide additional information or options while keeping users on the same screen.
- Prompting user response: Request user interaction or confirmation without a full page reload.
How to use
Creating a modal
- Access T4: Go to t4.vcu.edu and navigate to the page you want to update.
- Select: Choose the "Plugin - Modal" content type.
- Enter required information:
- Name: This is for internal use and will not be visible to users.
- Title: The title that will appear at the top of the modal window.
- Content: The main content that will be displayed inside the modal.
Linking a modal
- Navigate to content: Go to the T4 content type where you want to place the modal link.
- Insert modal link:
- Highlight the link text and choose "Insert content link" from the WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) menu.
- Select the page where the modal is saved and then choose the specific modal content you want to link.
Tips
- Content: Anything you can use in a general content WYSIWYG can be displayed inside the modal.
- User interaction: Modals must be triggered by user actions, such as clicking a button or following a link; they cannot load automatically.
- Use sparingly: Since modals interrupt the user’s workflow, use them only when necessary to avoid disrupting the user experience.
Requirements
- Name: Provide a name for the modal component.
- Title: Displayed at the top of the modal window.
- Content: The content to be shown inside the modal.
Accessibility considerations
- Unique title: Ensure each modal has a unique title that clearly describes its content.
- Descriptive links: Use meaningful text for links that trigger the modal to inform users about the modal’s purpose.
- ARIA labels: For links with identical text, use aria-labels to differentiate them for screen readers.
- Accessibility standards: Ensure that all content within the modal meets web accessibility standards.